
- SPIRAL Project
- Description
- Launcher plane (GSR)
- Orbital plane (OS)
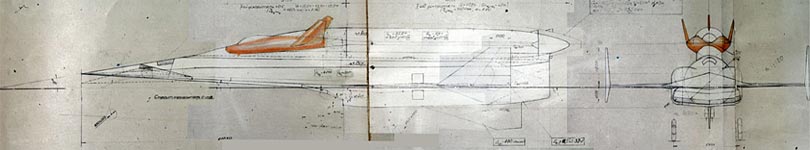
- Description
- Characteristics
- Composition
- Analogue plane (EPOS)
- Gallery
| -The Mriya is destroyed. |
| -Shipping of Buran-KS to Sotchi. |
| -Antonov is no more. |
| -Buran is now a museum. |
| -New pictures of the blogger Ralph Mirebs. |
Orbital space-plane
The landing was carried out by 4 skis located in the cold part, in the top area of the heat shield.
The engine part made up of:
- A GRD engine for orbital moving of 1.5 tf (320 s of specific impulse, fuel consumption of 4.7 kg/s), which makes it possible to the plane to change orbit and to start the impulse of braking for re-enter; it was envisaged thereafter to install of more powerful engines of 5 tf and 1.5 tf for the orbit correction.
- 2 emergency braking GRD engines of 16 kgf using pressurized special tanks.
- the orientation block including 6 orientation engines of 16 kgf and 10 accuracy engines of 1 kgf.
- a TRD engine of 2 tf and consumption of 1.38 kg/(kg.h) for the atmospheric flight and the landing running on kerosene. The air intake is located at the base of the vertical stabilizer (opened only during the engine working).
The cockpit, equipped by solid propellant motors, could eject to save the pilot in the event of damage in any phase of the flight. The capsule was equipped with an engine to direct it during the phase of re-entry in the atmosphere, with a beacon of rescue and batteries. The descent is done thanks to a parachute at the speed of 8 m/s, it is the deformation of the cabin which make the absorption of the landing shock.
Various models of orbital fighters
To be multipurpose the orbital fighters had a compartment of 2 m³which enabled them to embark various types of apparatuses such as a camera, a spreadable radio antenna, a space-ground missile, a space-space missile.
The day scout
 |
The day scout was intended for the fast detailed terrestrial and marine recognition target. The camera installed on the aircraft makes it possible to take details of 1.2 m at an altitude of 130 km more or less 5 km. It is supposed that the pilot seeks the objective manually by scanning the ground surface with a special sight, laid out in the cabin, having a zoom of 3x to 50x. |
The trigger of the camera is done by the pilot, the photographed zone is a square of 20 km for a limited altitude of 100 km. In a revolution the pilot must be able to shoot 3 or 4 objectives.
The day scout is equipped with KV and Уu1050 Вtransmitters to transmit information to the ground.
The day scout made of a welded frame, interior reinforcements, wings reinforcements, GRD, fuel tanks and blocks of equipment, of camera, TRD and air-flue, radio transmission system, cabin, mechanical actuators of the wings, vertical stabilizer, room of the main landing gear, air-brake, removable panel of the machines, lid of the camera and apparatuses of astronavigation.
Below the cyclo-gram is a standard flight of the day scout, dated of December 1965, we can see that the apparatus was not simply intended to took photograph but also for the orbital combat, in particular by the execution of anti-machine operations:

The radar scout
 |
The distinctive feature of the radar scout was the presence of a spreadable antenna of 12 x 1.5 m. The resolution supposed was to be from 20 to 30 m what is enough for the recognition of maritime embarked connections and also large terrestrial objects. |
The orbital shock space-plane - "the storm of the aircraft carriers"
 |
This plane was intended for the destruction of mobile marine objectives by launching a nuclear missile space-ground Бu1063 . The precises coordinates of the objective was defined by the embarked radar and the navigation means of the space-plane. The piloting of the missile by radio made it possible to correct the trajectory errors in the first moments of flight. The missile had a mass of 1.7 t and its ray of destruction was of more or less 90 km, which is enough to destroy an aircraft carriers which sails at 32 knots. |
Space interceptor "50-22".
 |
The last alternative of combat of the orbital space-plane was a space interceptor (2 alternatives were studied): |
- The objective was to come near the target at a distance of 3 to 5 km and to synchronize its speed with the target. Then the pilot could make an inspection of the target with the sight 50x (resolution of 1.5-2.5 cm) and also take photographs.
If the pilot was to eliminate the target the plane is equipped with 6 self-guiding missiles of type Сu1050 БМu1054 П weight 25 kg, of autonomy of 30 km and speed 500 m/s, ensuring the total destruction of the objective. The autonomy of the plane was enough to ensure the destruction of objectives until 1000 km heights, as well as orbits of 10° compared to that of the plane. - The other alternative was the interceptor equipped with self-directed Сu1050 БМu1054 Пmissiles for the destruction of objectives, weight of 170 kg, an autonomy of 40 km and a maximum altitude of setting fire of 350 km. Detection as well as the setting with fire of the missile was made by the pilot thanks to the sight. The autonomy of the space-plane was enough to intercept 2 objectives until an altitude 1000 km.
